Embark on a journey through the prosperous realm of Gap Trading Strategies with our comprehensive guide. Discover the art of recognizing and profiting from market gaps, arising from overnight developments or other impactful events. Within this article, we delve into established techniques and valuable insights designed to assist traders in navigating the distinctive opportunities and challenges inherent in gap trading.
What is gap?
In straightforward terms, traders pinpoint gaps in trading charts, indicating volatile price movements between opening and closing prices. This identification serves as a foundation for crafting effective trading strategies, requiring the calculation of potential buy and sell points. Traders commonly employ event-based strategies in the presence of market gaps, allowing them to make predictions about future developments.
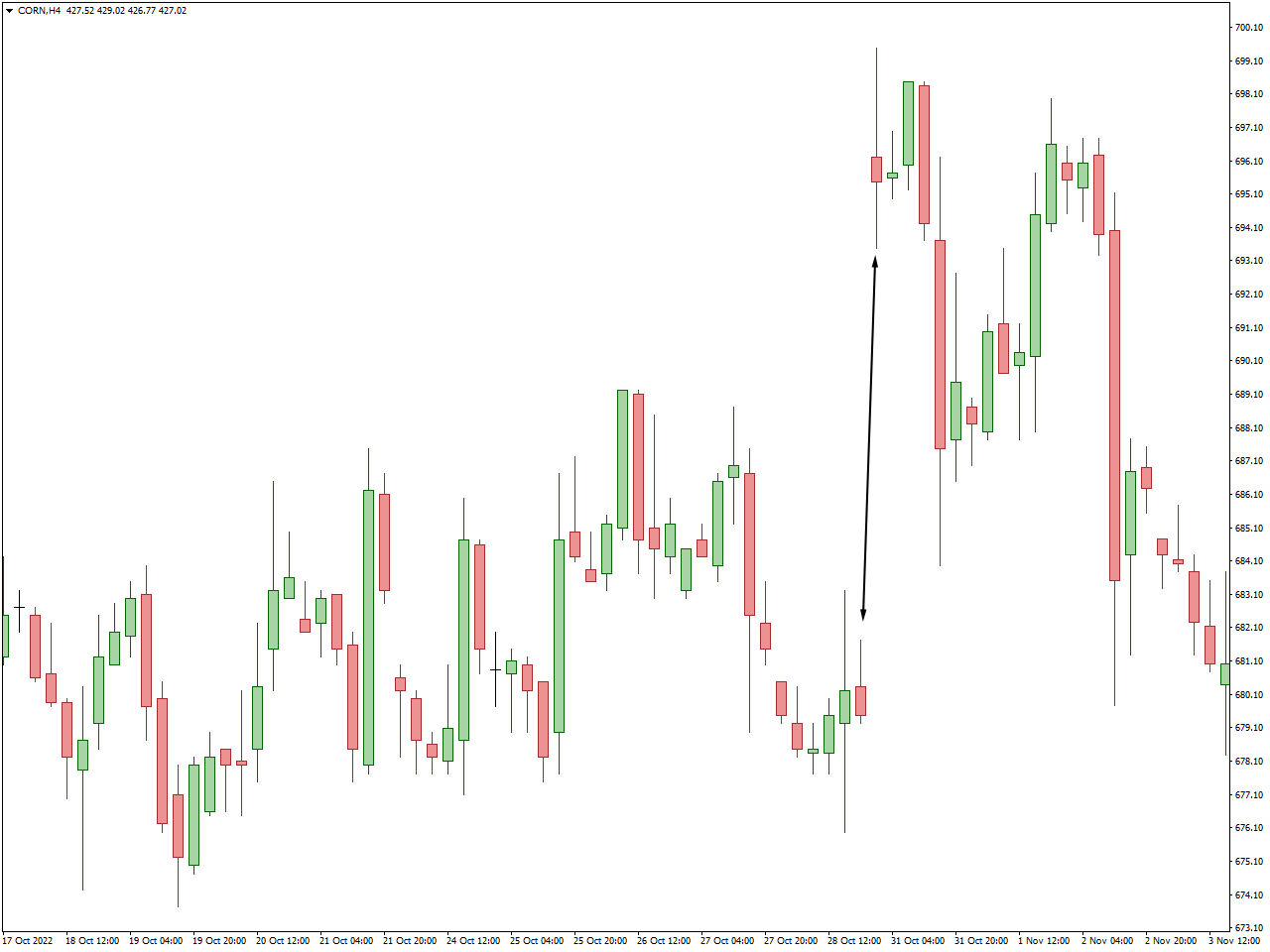
How to find gaps?
Identifying gap-up stocks and currency pairs is relatively straightforward on a price chart. Market gaps are visually represented as vacant spaces between candlesticks, and gap-up stocks and forex pairs are characterized by the appearance of a red candlestick at the opening. This occurrence signifies a price rally, indicating the possibility of a new trend or potentially highlighting an anomaly. For instance, in the example below, a substantial gap in the price chart is succeeded by a red candle, suggesting that an external event has triggered a significant bearish movement in the asset’s price.
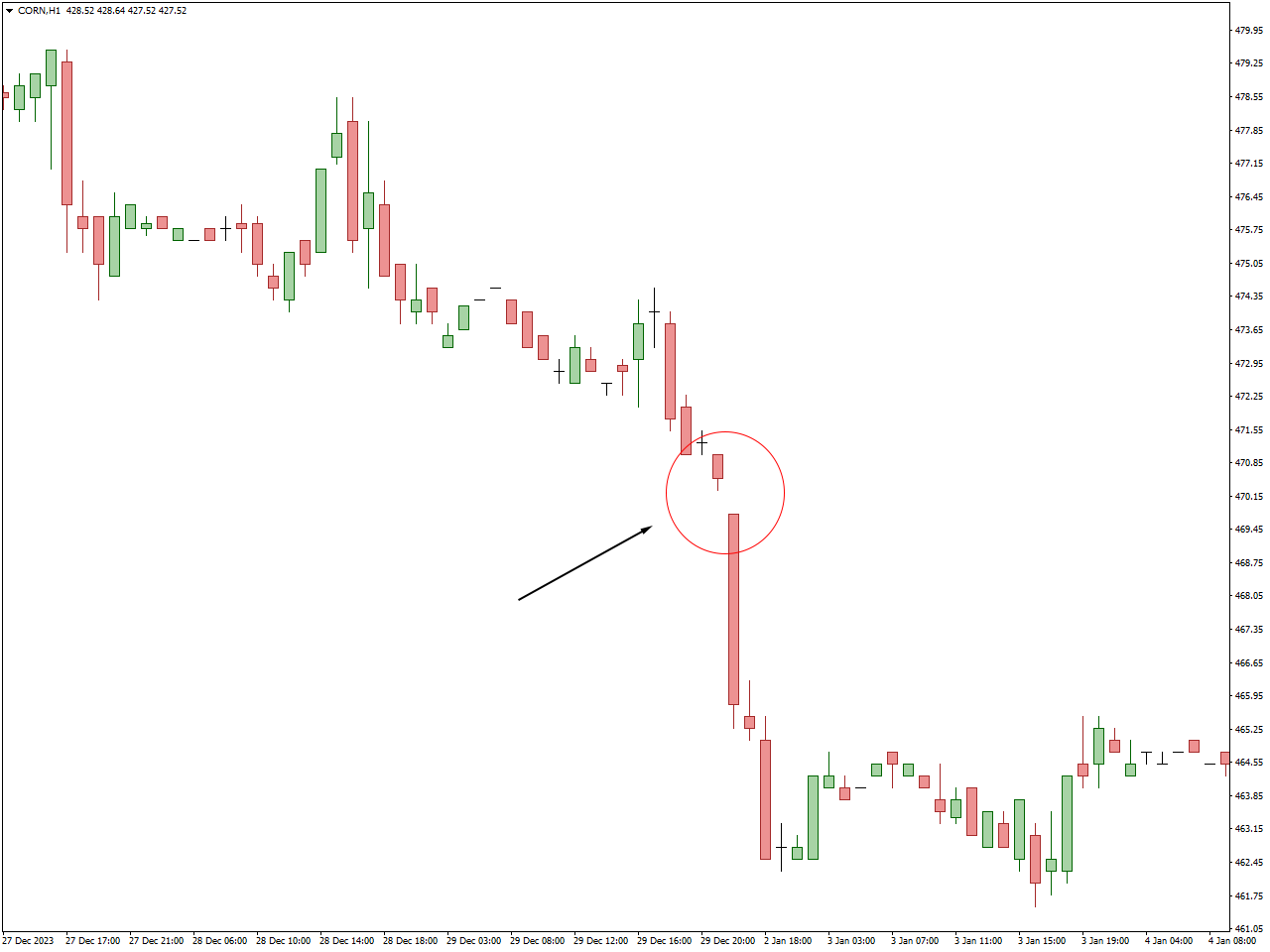
What causes gaps?
Gaps can arise from various factors, with their occurrence often attributed to unforeseen news developments or a breach of technical support or resistance.
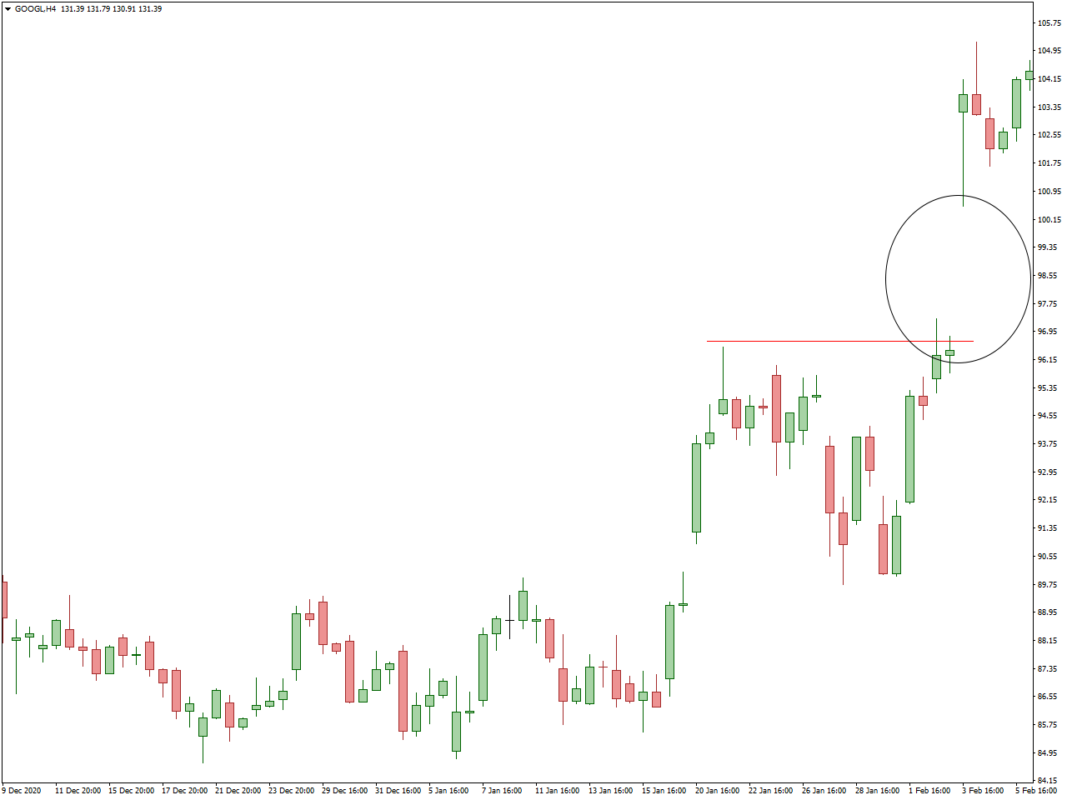
From a fundamental perspective, the catalyst for gaps may stem from noteworthy events like a company surpassing earnings estimates significantly or a significant speech by a Federal Reserve (Fed) official influencing expectations regarding interest rates.
On the technical front, gaps can emerge following the breach of a previous high/low or the violation of other technical indicators like resistance or support levels, including pivotal trend lines.
Establishing Technical Analysis Foundations and Identifying Opportunities
Excelling in gap trading requires a solid grasp of technical analysis, covering chart patterns, volume, support and resistance levels, and key indicators like moving averages and RSI. A thorough examination of historical forex price trends acts as a valuable foundation for anticipating how the market might respond to future gaps. Recognizing patterns such as breakaway or exhaustion gaps is pivotal, underscoring the accurate interpretation of their implications. Proficiency in using technical analysis tools is essential for assessing gap strength and its potential impact on currency prices. Successful gap trading relies on precise data interpretation and indicators, going beyond mere gap recognition.
Identifying gaps necessitates vigilance and the use of appropriate tools. Traders can leverage charting software that provides a comprehensive view of price movements across various time frames. Monitoring after-hours and pre-market trading activities provides early insights into potential gaps. Additionally, using scanners capable of filtering currencies experiencing gaps proves advantageous. It’s crucial to recognize that not all gaps hold equal significance, and a trader’s skill lies in discerning opportunities based on factors like volume, gap size, and the broader context of market sentiment.
Mastering Gap Trading Strategies
Currency pairs, pips, and the forex market are integral components of trading. Technical analysis involves studying candlestick charts, employing various trading strategies, and analyzing price action. Traders rely on forex signals, chart patterns, and diverse approaches like scalping, day trading, and swing trading.
Managing risk with a favorable risk-reward ratio is crucial, incorporating fundamental analysis and understanding trading psychology. Choosing reputable forex brokers and a suitable trading platform, along with expert advisors (EAs) and backtesting, contribute to a trader’s success. Leverage and margin play roles in establishing long or short positions, and utilizing stop-loss and take-profit orders.
Market orders, pending orders, and considerations of volatility and liquidity shape trading decisions. Money management strategies are vital, encompassing trading sessions, currency correlation, economic calendars, and market sentiment. Support and resistance levels guide trades, while risk management strategies and effective use of trading software are key.
Price charts, forex news, and identifying price trends are fundamental. Distinguishing trend-following strategies, divergence, and catering to beginners in technical forex trading are essential. Implementing a trading strategy involves signals, arrows, buy/sell indications, bars, bearish/bullish trends, and support/resistance zones. Utilizing lines and zones in intraday, daily, weekly, and monthly trading, installing automatic alerts, and recognizing breakout trends are critical.
Metatrader, with its automatic and super channels, facilitates trading positions with low and high daily/weekly/monthly levels. Installing classic trade charts, employing trendlines, considering volume, ticks, stocks, and the repaint/non-repaint aspect of indicators like MTF fractals contribute to successful trading. Spread management is an additional aspect that requires attention in trading.
Here are a few common gap trading strategies:
Common Gap Trading involves small price gaps that regularly occur and are considered a natural part of market movements. Traders may establish positions with the expectation that the gap will eventually be filled, moving towards the previous closing price. If the gap is bullish, traders might take a short position, and if it’s bearish, they may opt for a long position.
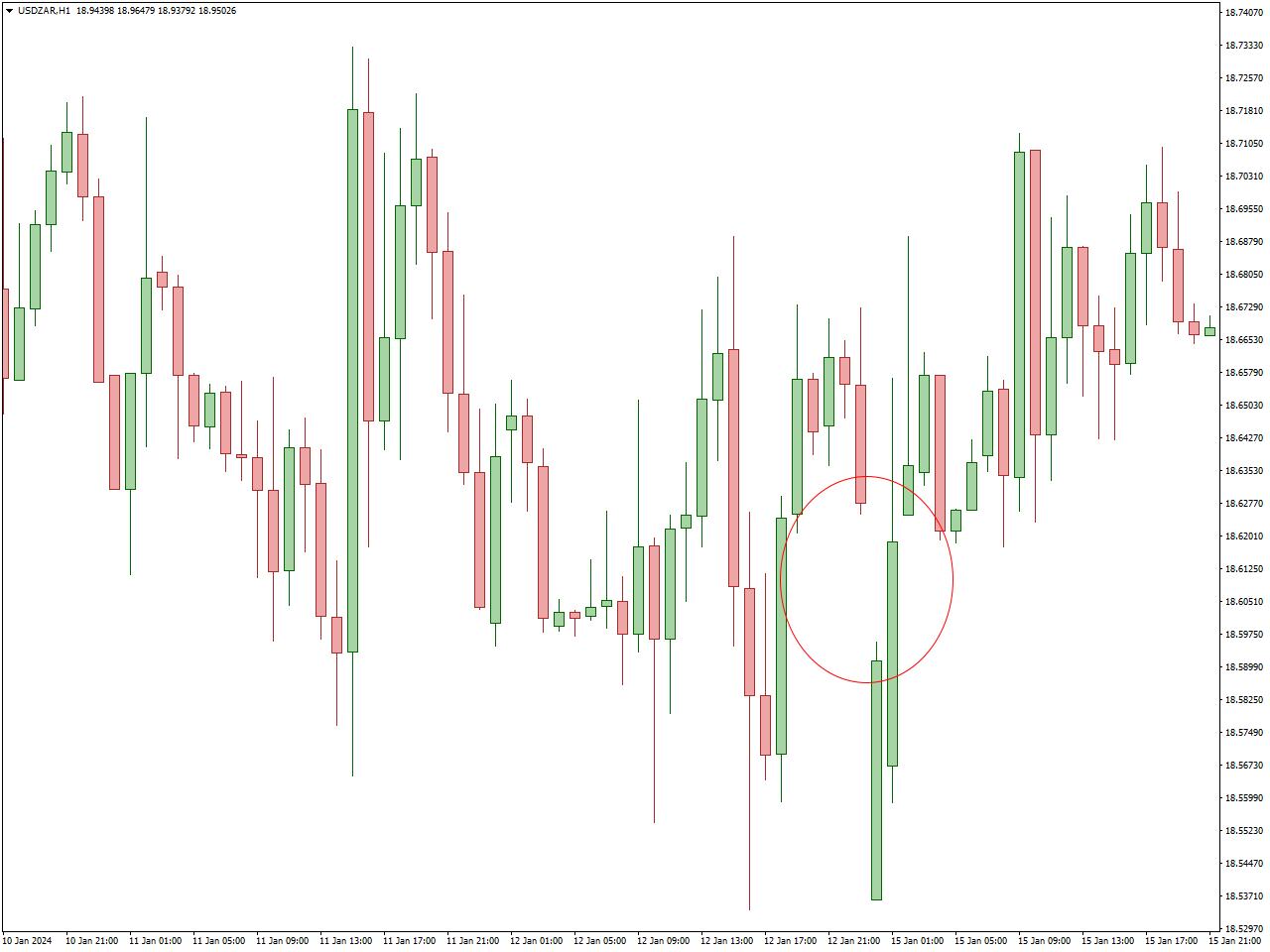
Breakaway Gap Trading comes into play when the price breaches a significant support or resistance level, signaling a new trend. Traders may position themselves in the direction of the gap, anticipating a sustained trend. These gaps often come with robust momentum, and traders seek to leverage this momentum to their advantage.
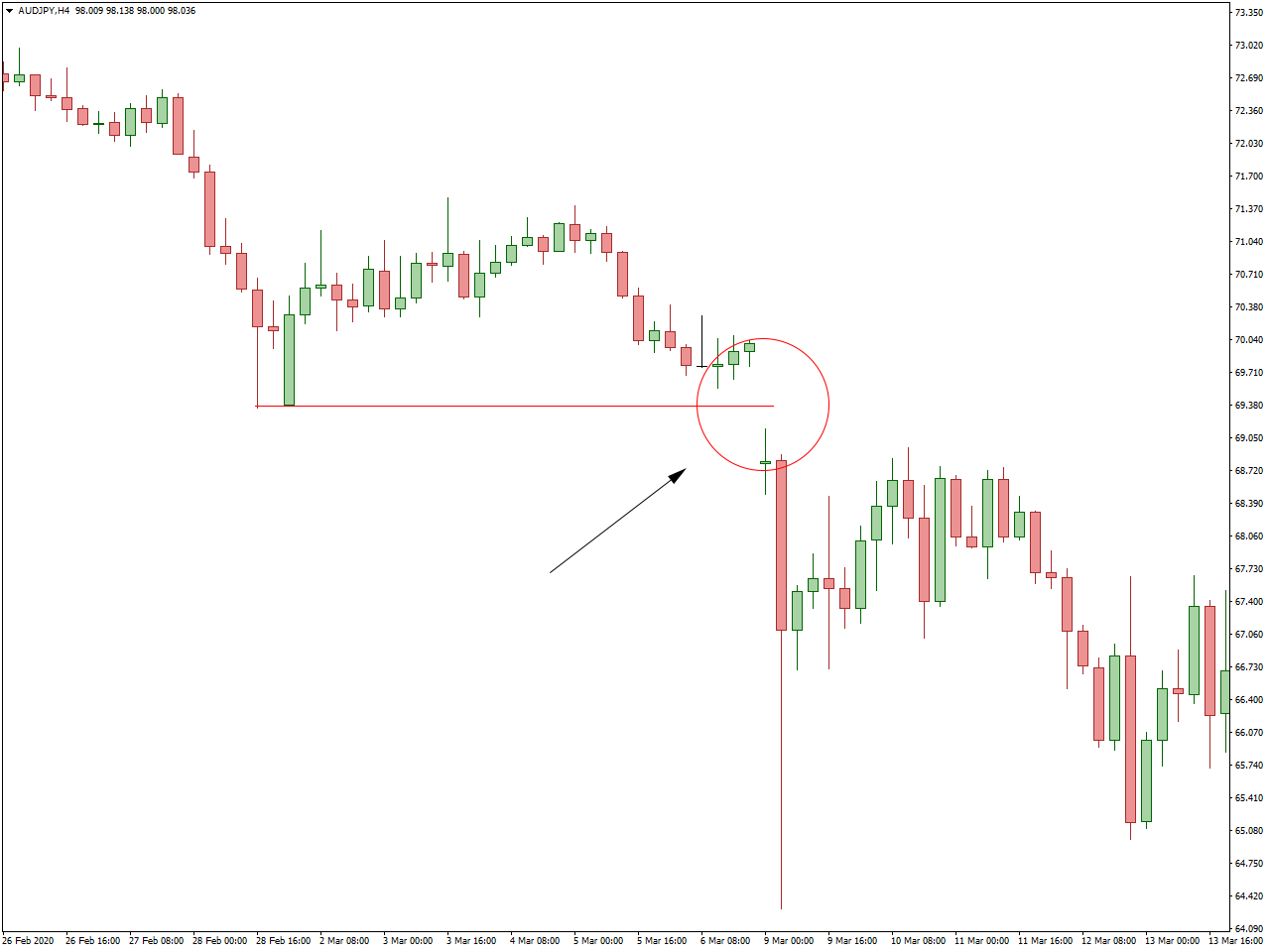
Runaway (Continuation) Gap Trading is applied when gaps occur in the middle of a trend, indicating a continuation of the existing price direction. Traders may enter positions aligned with the prevailing trend, expecting it to persist. This strategy hinges on the belief that the momentum suggested by the gap will endure.
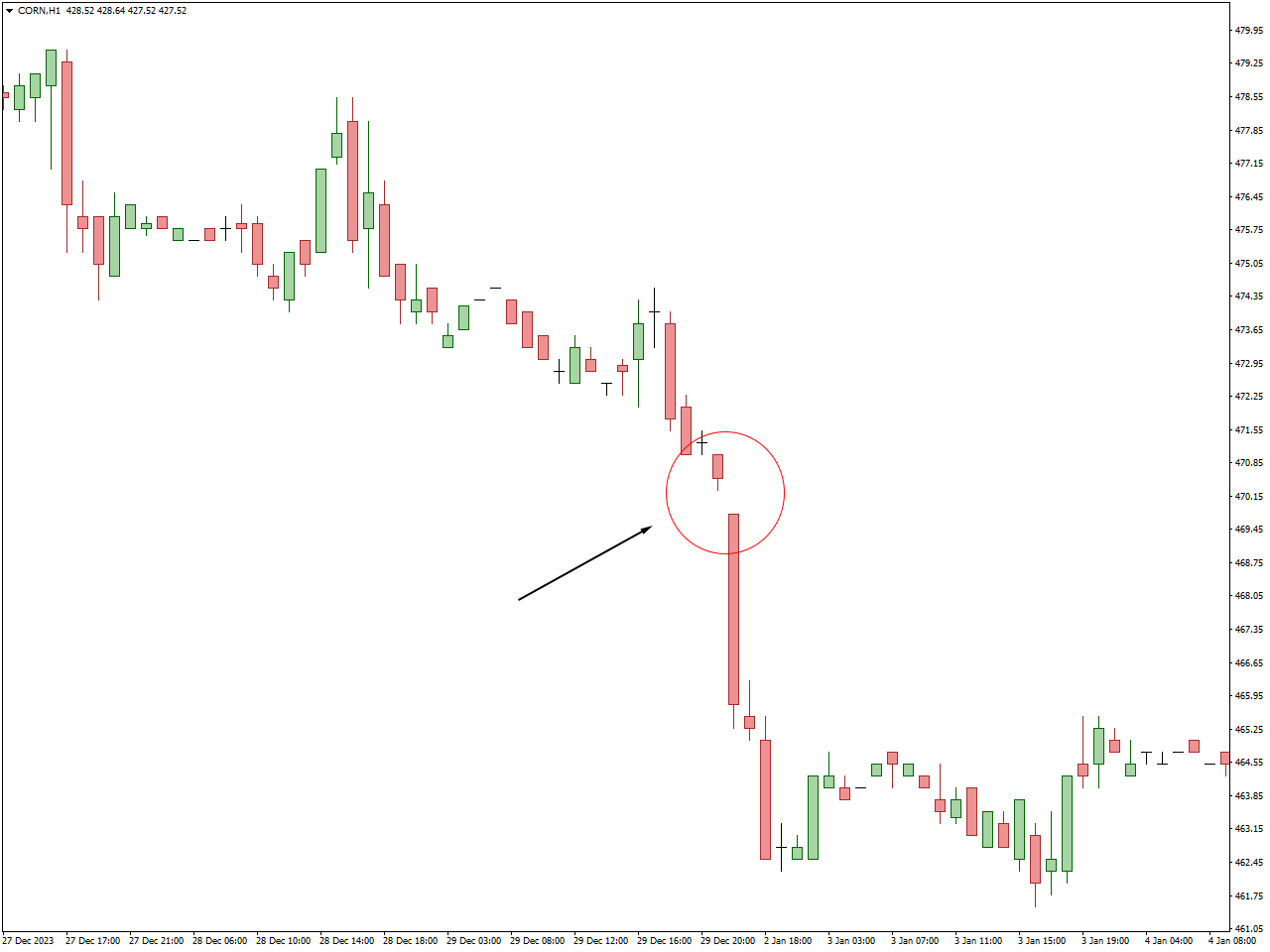
Exhaustion Gap Trading focuses on gaps near the end of a strong trend, suggesting a waning momentum in the existing trend. Traders may take positions opposing the prevailing trend, anticipating a reversal. This strategy is based on the notion that the gap represents a final surge in buying or selling before a reversal takes place.
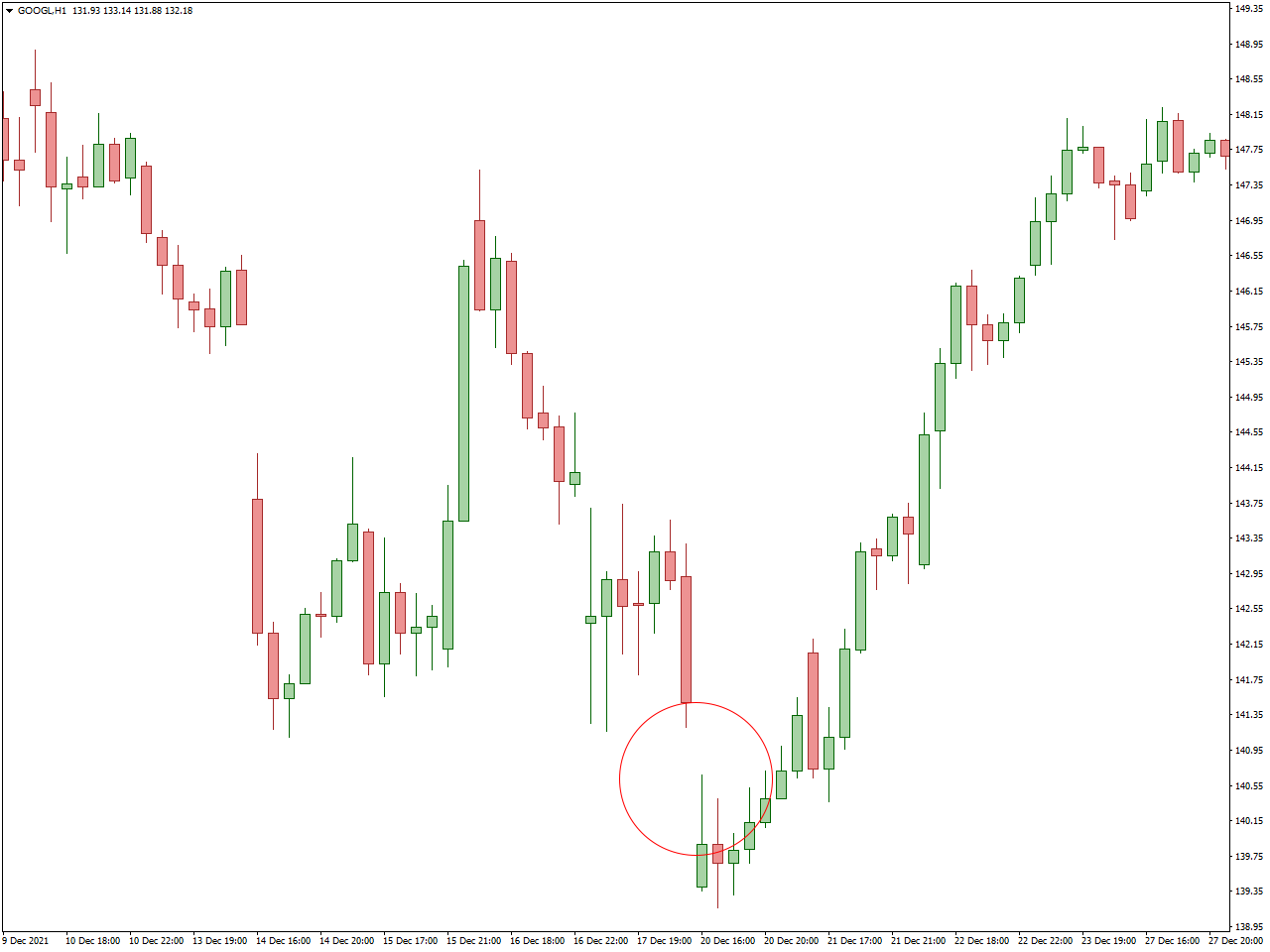
Island Reversal Gap Trading is relevant when a price gap isolates a previous price movement, forming a “gap island.” Traders may interpret this as a potential signal for a trend reversal. Positions are often taken in the opposite direction of the previous trend, with an expectation of a shift in market sentiment.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our investigation into Gap Trading Strategies, you will have acquired a profound comprehension of leveraging the potential profits inherent in market gaps. Equipped with established techniques, effective risk management strategies, and a keen understanding of market behavior, you’ll be well-prepared to navigate the dynamic landscape of gap trading. Stay at the forefront of the market and enhance your trading voyage with the knowledge and skills acquired from this all-encompassing guide.

