In the fast-paced world of the forex market, traders often engage in strategies that can be broadly categorized into day trading and intraday trading. Both approaches focus on short-term price movements, but there are distinct nuances and methods that set them apart. This article delves into the similarities and differences between day trading and intraday trading, using key concepts and terminology relevant to forex trading.
Similarities Between Day Trading and Intraday Trading
Short-Term Focus: Both day trading and intraday trading aim to capitalize on short-term price movements within the same trading day, avoiding overnight risk by not holding positions after market close. However, intraday trading is closer to scalping, involving even quicker trades and more frequent transactions compared to the broader strategies typically employed in day trading.
Technical Analysis: Traders rely heavily on technical analysis, including the use of candlestick charts, chart patterns, and indicators to make informed decisions. Candlestick charts provide visual representations of price movements over specific periods, helping traders identify potential market trends and reversals. Chart patterns, such as head and shoulders or double tops and bottoms, offer insights into possible future price directions based on historical price behavior. Tools like price action, which involves studying historical price movements without relying on lagging indicators, support and resistance levels, which highlight areas where the price is likely to encounter obstacles, and trendlines, which indicate the direction of the market trend, are commonly used.
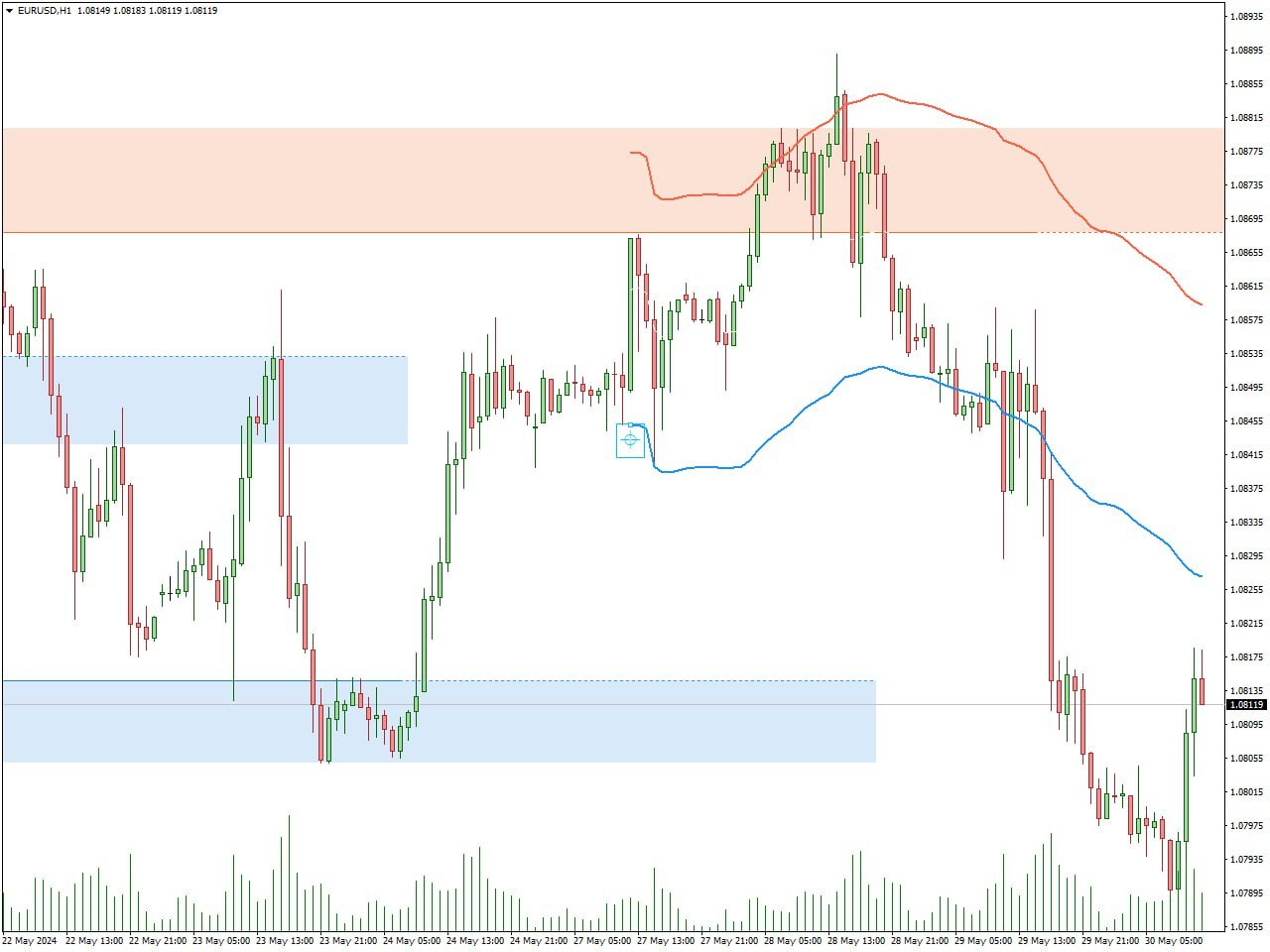
Here you can see support and resistance levels indicator in pair with Anchored VWAP. Support and resistance levels, combined with the Anchored VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price), provide buy and sell signals in trading. When the price approaches a support level, which is often below the current market price, it signifies a potential buy signal as the price is likely to bounce back up from this level. Conversely, when the price nears a resistance level, typically above the current market price, it indicates a potential sell signal as the price may reverse downward from this point. The Anchored VWAP adds another layer of analysis by indicating the average price of the asset, adjusted for volume, from a specific starting point. When the price is above the Anchored VWAP, it suggests a bullish trend, supporting buy signals at support levels, whereas a price below the Anchored VWAP implies a bearish trend, reinforcing sell signals at resistance levels. Combining these indicators helps traders make more informed decisions by aligning price action with volume-weighted averages and critical price levels.
Risk Management: Effective risk management strategies, including setting stop-loss orders and take-profit orders, are crucial for successful trading. By setting stop-loss orders, traders can limit potential losses by automatically closing a position when the market moves against them to a certain extent. Similarly, take-profit orders enable traders to lock in profits by automatically closing a position once it reaches a predefined price level. These tools help traders optimize their risk-reward ratio, ensuring that potential gains are maximized while minimizing possible losses. Through careful planning and disciplined execution of these strategies, traders can navigate the volatile forex market with greater confidence and control, ultimately enhancing their overall trading performance and sustainability.
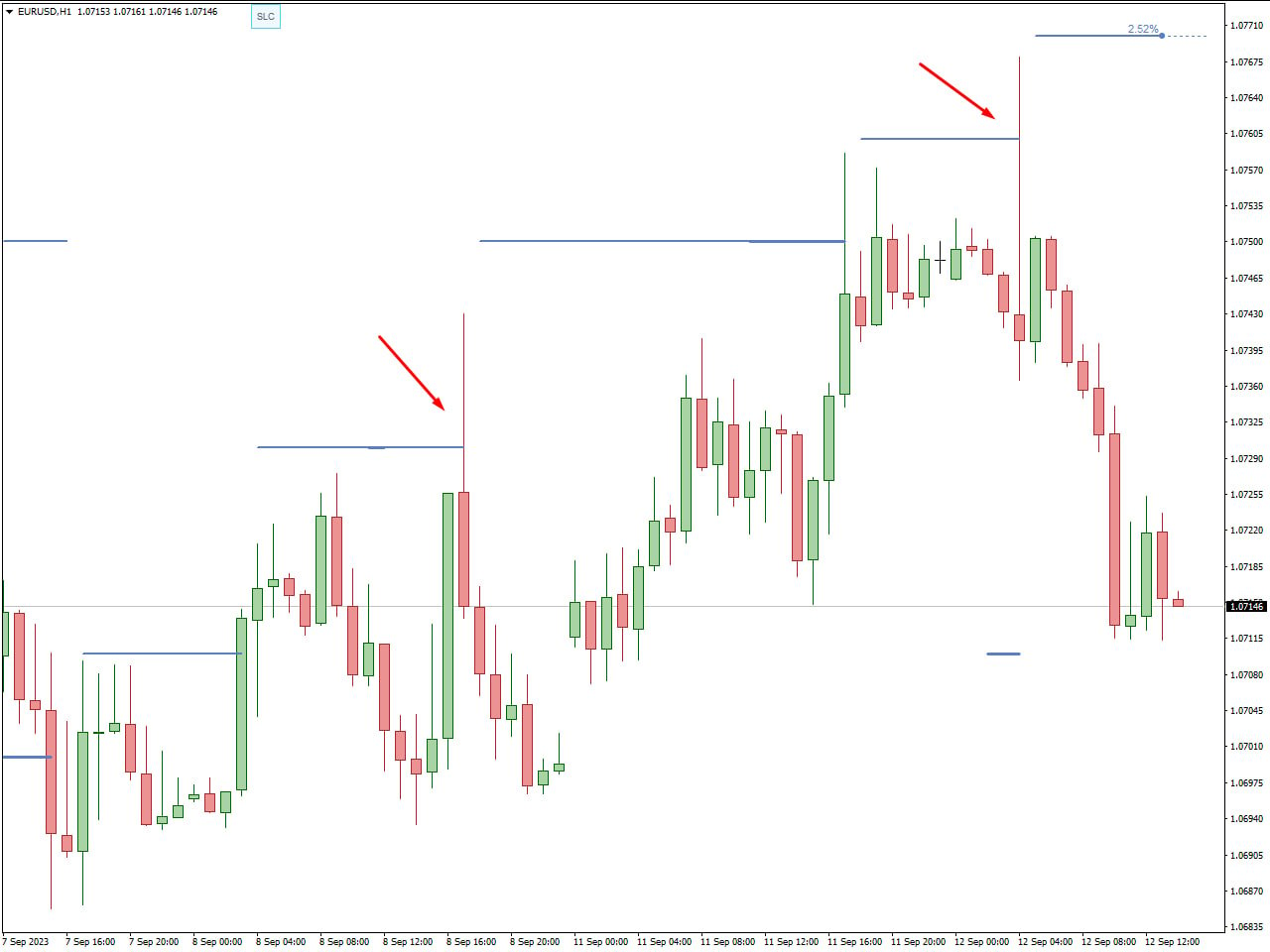
One advantageous strategy in trading is to leverage the stop losses set by other traders. The FXSSI Stop Loss Clusters Indicator can be an invaluable tool for this purpose. By analyzing the clusters of stop loss orders, you can strategically place your buy or sell orders nearby. When these stop loss clusters are triggered, it often results in short-term price swings, allowing you to capitalize on these market movements. For instance, if you identify a cluster of stop loss orders for long positions, placing a sell order just above this cluster can be profitable. As the price approaches and triggers these stop losses, the resulting sell-off can create a sharp downward movement. Conversely, placing a buy order just below a cluster of stop loss orders for short positions can allow you to benefit from a quick price surge as these stop losses are hit. Using the FXSSI Stop Loss Clusters Indicator enables you to pinpoint these strategic entry points, enhancing your ability to profit from short-term market fluctuations. This approach not only improves your chances of making profitable trades but also helps you better understand market sentiment and the behavior of other traders.
Trading Strategies: Both trading styles utilize various trading styles such as scalping, which involves making numerous small trades to profit from minor price changes. Scalping requires traders to execute a high volume of trades within short time frames, often seconds to minutes, aiming to take advantage of small fluctuations in currency pairs. This strategy demands quick decision-making and precise execution to accumulate profits from many small gains. On the other hand, trend-following strategies involve identifying and following the direction of significant price trends, whether upward or downward, over a longer period within the trading day. There are also different types of trading days include trend days, where the price moves consistently in one direction; reversal days, where the price starts in one direction but reverses sharply; range days, where the price oscillates within a defined range between support and resistance levels; and volatile days, characterized by large price swings in both directions. Understanding these tendencies and types of trading days helps traders employ appropriate strategies and make informed decisions. Traders employing trend-following techniques analyze market trends using technical indicators, chart patterns, and price action to enter and exit trades at optimal points, seeking to ride the trend for more substantial profits. Both approaches necessitate a thorough understanding of technical analysis, market conditions, and effective risk management to be successful in the dynamic forex market.
Trading Platforms and Software: Day traders and intraday traders often use advanced trading platform like MetaTrader, which provide real-time data. This platform is integral to executing and managing trades efficiently in the fast-paced forex market.
Differences Between Day Trading and Intraday Trading
- Time Frame: The timeframe distinguishes intraday trading from day trading. Day trading involves opening and closing all positions within the same day, typically holding trades for minutes to a few hours to avoid overnight risks. Intraday trading also focuses on same-day trades but is closer to scalping, involving very quick trades and more frequent transactions. Positions are typically held for just minutes to a few hours, depending on market conditions and strategies, offering less flexibility compared to broader day trading approaches.
- Trading Volume and Frequency: Day traders typically engage in higher trading volume and frequency, executing many trades to exploit market volatility. Intraday traders might trade less frequently but aim for more substantial price movements within the day.
- Strategy Complexity: Day trading strategies can be more complex, incorporating advanced technical analysis, forex signals, and automated trading systems. Intraday trading might rely more on simpler, straightforward strategies like breakout trading and using forex signals for entry and exit points.
- Market Orders and Pending Orders: Both trading styles use market orders and pending orders, but day traders often prefer market orders to capitalize on immediate price movements. Intraday traders might use more pending orders to enter trades at specific levels as per their analysis.
- Psychological Pressure: The rapid pace of Intraday trading can exert significant psychological pressure, demanding quick decision-making and mental resilience. Day trading, while still demanding, may offer slightly less pressure due to the longer holding periods within the trading day.
Key Concepts in Day Trading and Intraday Trading
Day trading and intraday trading involve the rapid buying and selling of financial instruments within the same trading day, with the goal of capitalizing on short-term price movements. Central to these practices are market timing, volatility, and liquidity. Traders exploit periods of high volatility, especially around the market opening and closing hours, as these times often present the most significant price swings. High liquidity is also essential, ensuring that trades can be executed quickly and efficiently without significantly affecting the asset’s price.
Technical analysis is a cornerstone of day trading, with traders relying on chart patterns and indicators such as moving averages, Bollinger Bands, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and support and resistance levels to predict market trends and identify optimal entry and exit points. These tools help traders to make informed decisions based on historical price data and market sentiment. Effective risk management strategies, including the use of stop loss and take profit orders, are crucial to limit potential losses and secure profits. Position sizing, or determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to a single trade, is also a key aspect of managing risk.
Psychological discipline is perhaps the most critical component of successful day trading. Traders must maintain emotional control, adhering strictly to their trading plans and strategies without succumbing to the impulsive decisions driven by market fluctuations. Consistency and discipline in following a well-defined trading strategy, combined with a thorough understanding of market mechanics and technical analysis, are essential for long-term success in day trading.
Conclusion
Day trading and intraday trading share many similarities, primarily their focus on short-term market movements and reliance on technical analysis. However, they differ in terms of time frames, trading volume, order quantity, strategy complexity, and psychological demand. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding these differences and similarities can help you choose the trading style that best suits your goals and risk tolerance. With the right trading strategies, tools, and mindset, both day trading and intraday trading can be profitable approaches in the dynamic forex market.

