Swing trading and day trading are two well-known strategies employed by traders to benefit from short-term market fluctuations. Although both methods focus on leveraging price movements, they vary considerably in terms of timeframes, trading frequency, and tactics. Below is a detailed comparison of swing trading and day trading to assist you in determining which strategy aligns better with your trading style and objectives.
Swing Trading
Swing trading is a short- to medium-term trading strategy where traders aim to capture gains by capitalizing on the price swings of a financial instrument, typically over a few days to several weeks. It relies heavily on technical analysis, using indicators and chart patterns to identify potential entry and exit points. Swing traders seek to exploit trends, whether upward or downward, by entering positions at key support or resistance levels and setting stop-loss orders to manage risk. With a focus on risk management and position sizing, swing traders continuously monitor their trades, adjusting their strategies as needed based on market conditions and performance. Through careful analysis and execution, swing trading aims to generate profits within a relatively short timeframe compared to long-term investing.
Key Characteristics:
Timeframe: Swing trading involves holding positions for a few days, offering a less frequent trading pace than day trading, which translates to fewer transactions over the same timeframe. This approach grants traders the flexibility to analyze markets and make decisions outside regular trading hours. Unlike day trading, swing trading doesn’t demand constant monitoring throughout the day, fostering a more balanced and manageable trading style.
Strategies: Swing traders often rely on technical analysis. Such instruments like moving averages can be very helpful in this way of trading. In the image below you can see 3 MA Cross with Alert MTF Indicator in action.
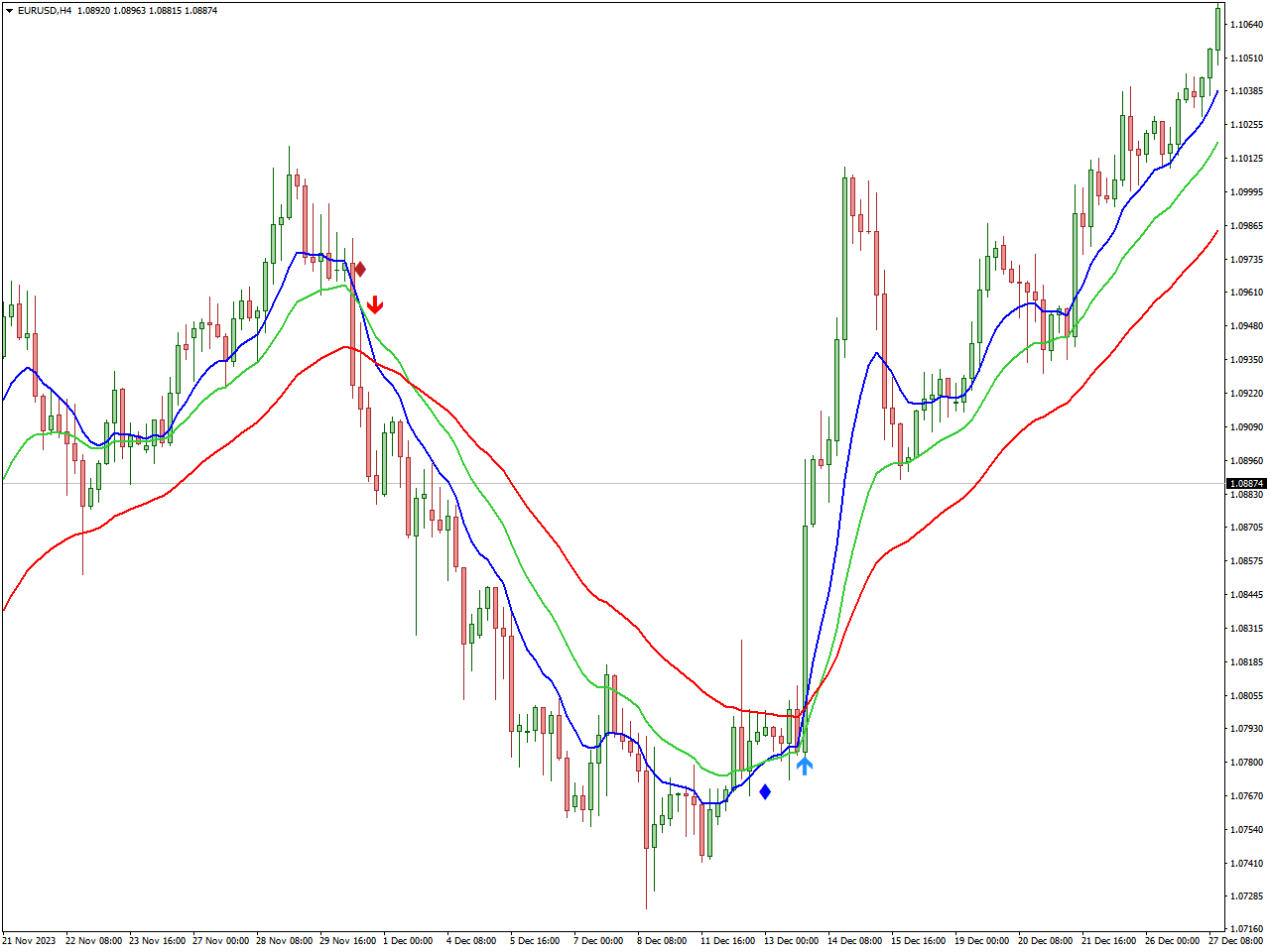
Risk-Reward Ratio: The longer holding periods in swing trading generally lead to lower stress levels for traders. There is potential for larger individual profits due to the ability to capture more significant price swings. However, traders are exposed to overnight risk, which can be managed using stop-loss order.
Examples of Swing Trading Tools: Swing traders utilize a variety of tools to effectively navigate the markets and capitalize on short- to medium-term price movements. These tools include advanced charting software like TradingView or MetaTrader, which provide essential technical analysis features such as customizable indicators and drawing tools for identifying trends and potential entry/exit points.risk management tools like position sizing calculators and trading journals assist in managing risk and analyzing trade performance. By leveraging these tools effectively, swing traders can make informed decisions, minimize risk, and improve their overall trading success. In the example you can see chart patterns generated by Bos & Choch indicator.
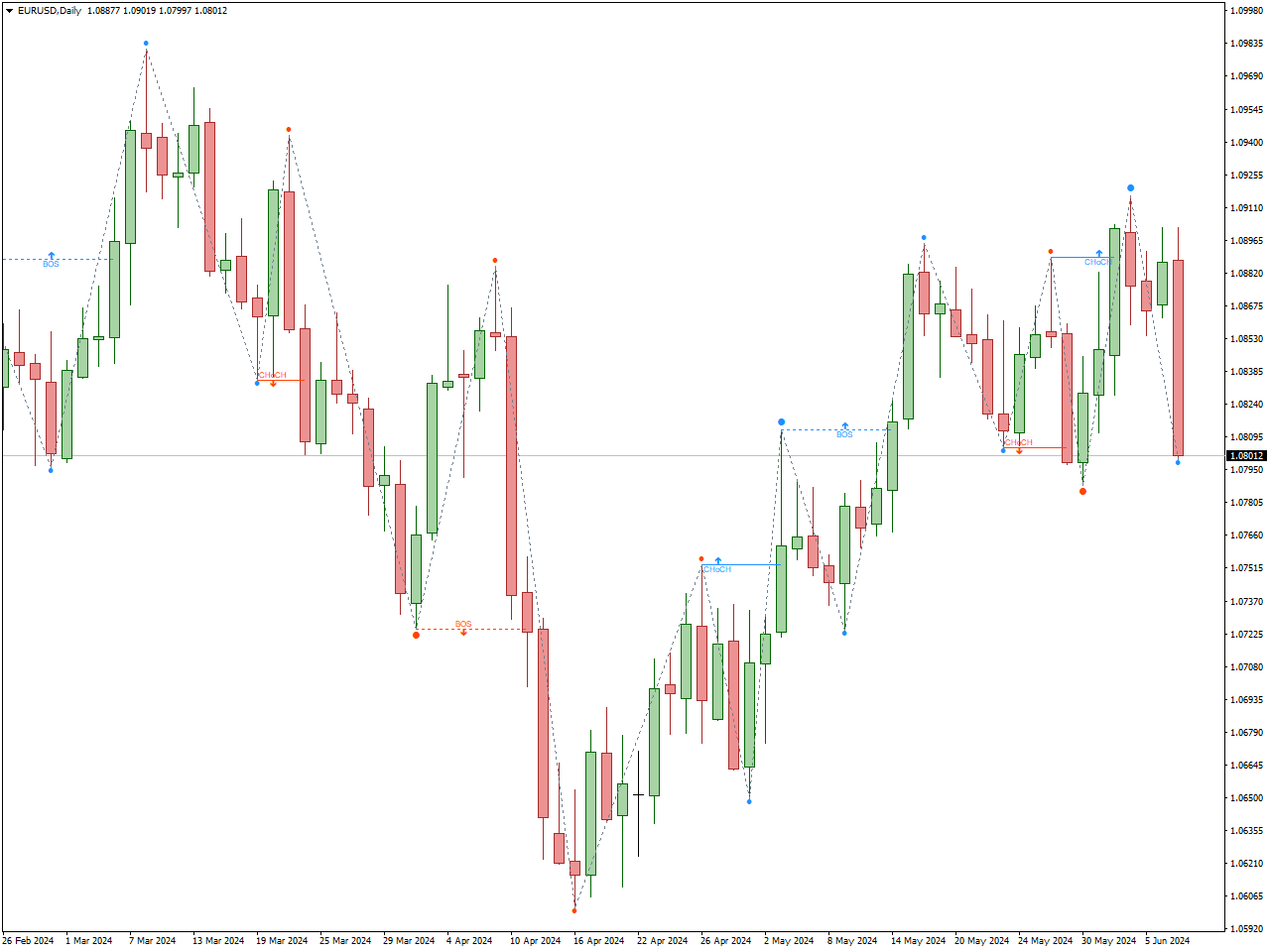
The Bos & Choch indicator is particularly beneficial for swing trading as it helps traders identify critical trend reversals and continuation patterns, crucial for capturing gains over a few days to weeks. The “Break of Structure” (BoS) aspect signals potential trend changes by identifying when the price breaks significant support or resistance levels, indicating new upward or downward trends. The “Change of Character” (ChoCh) component highlights when the market shifts from one trend to another, aiding traders in recognizing trend momentum loss and imminent reversals. This dual functionality provides clear entry and exit points, enabling swing traders to enter trades at the onset of new trends and exit before reversals, thus maximizing profit potential and minimizing risks.
Day Trading
Day trading involves the frequent buy and sell orders within a single trading day, with the aim of capitalizing on intraday price fluctuations. This strategy necessitates vigilant market monitoring and swift decision-making, heavily leaning on technical analysis tools such as intraday charts, VWAP, and moving averages. Although day trading offers the potential for regular, modest gains without overnight exposure, it demands a significant level of commitment, expertise, and emotional resilience due to its fast-paced nature and the necessity for prompt execution. It is most suitable for individuals able to devote their full attention to trading during market hours and effectively handle the associated stress and transaction costs.
Key Characteristics:
Timeframe: In day trading, positions are opened and closed within the same trading day. This approach involves high-frequency trading with multiple transactions occurring throughout the day.
Trading Hours: Day trading requires constant monitoring of the markets during trading hours. The process is intensive and fast-paced, demanding real-time decision-making.
Strategies: Day traders primarily rely on technical analysis, focusing on intraday charts such as 30-minute and 1-hour intervals. They use indicators like VWAP, moving averages, and MACD to track short-term price movements. Another strategy, momentum trading, involves capturing strong price movements based on volume spikes and news. Here you can see FXSSI.StopLossClusters indicator:
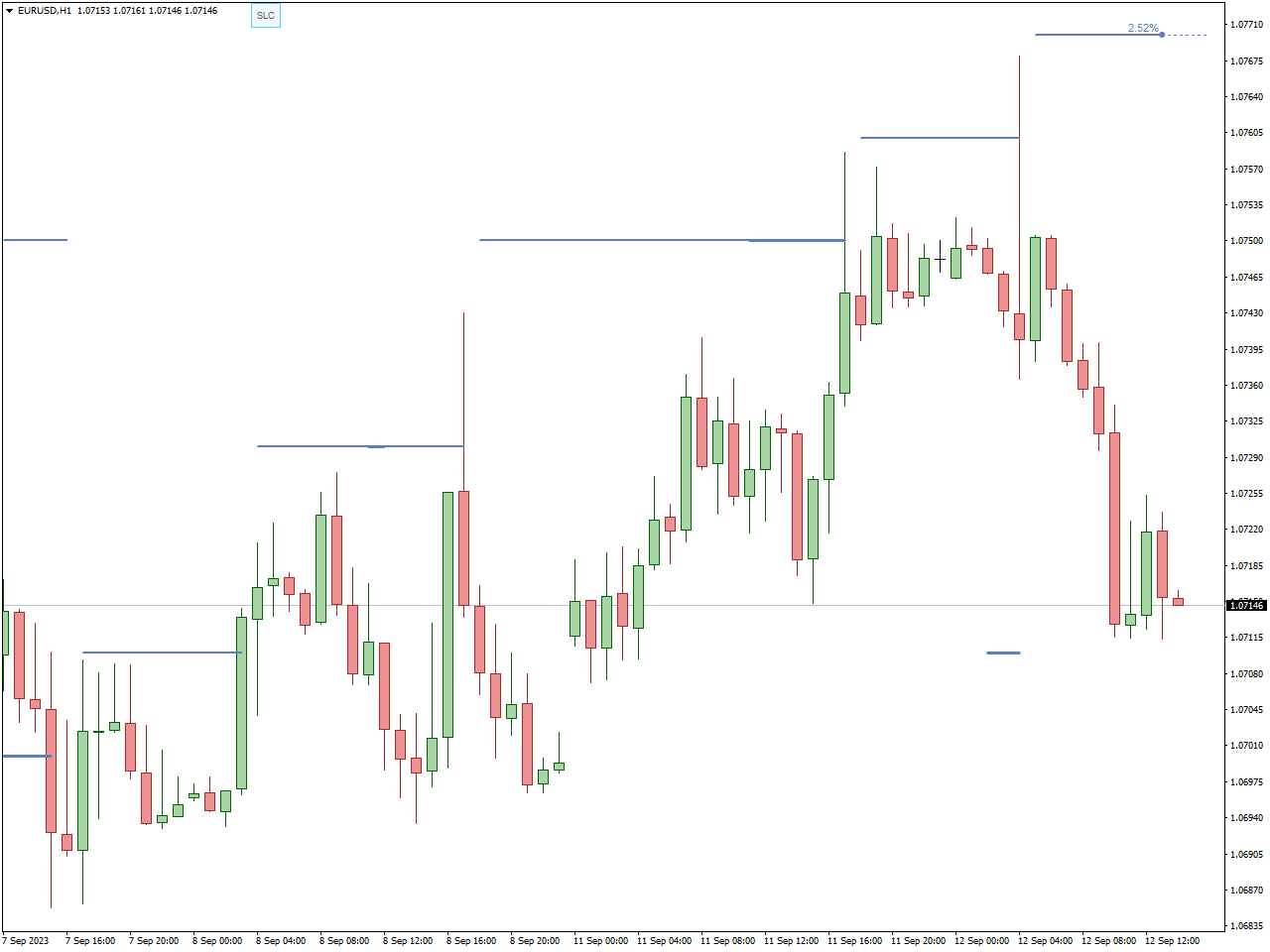
FXSSI.StopLossClusters indicator is highly advantageous for swing trading due to its ability to identify clusters of stop-loss orders placed by other traders at specific price levels. In swing trading, where positions are held for days to weeks, managing risk is paramount. This indicator helps traders anticipate areas of significant support or resistance based on where clusters of stop-loss orders are concentrated. By strategically placing stop-loss orders just beyond these clusters, swing traders can minimize the risk of premature exits during price fluctuations while potentially benefiting from price reversals that occur when these clusters are triggered. This approach enhances risk management and decision-making, allowing swing traders to better protect their capital and optimize their trading strategies for capturing favorable price movements over longer time frames.
Risk and Reward: The nature of day trading brings higher stress due to the need for quick decision-making. While this approach offers the potential for frequent small profits that accumulate over time, it eliminates overnight risk exposure, reducing the risk of unexpected news affecting position.
Examples of Day Trading Tools: Day traders utilize several tools to optimize their trading activities. Intraday charts help identify real-time trends and price action. Volume analysis is crucial for understanding the strength of price movements. Market order are used for the quick execution of trades to capitalize on short-term opportunities. In this example, Volume Profile Indicator proves invaluable in swing trading as it visualizes the distribution of trading volume across specific price levels over a defined period, typically displayed as a histogram on the price chart’s vertical axis. This tool offers swing traders crucial insights into where significant buying or selling activity occurs within a given range, highlighting key support and resistance levels that may influence price behavior. By identifying areas with the highest volume (known as high-volume nodes) and low-volume areas (low-volume nodes), traders can make informed decisions about entry and exit points, manage risk more effectively by placing stop-loss orders near high-volume nodes, and potentially anticipate price movements based on the volume-based support or resistance. This depth of analysis enhances the trader’s ability to strategize trades that align with market dynamics, contributing to more informed and potentially profitable trading decisions in swing trading scenarios.
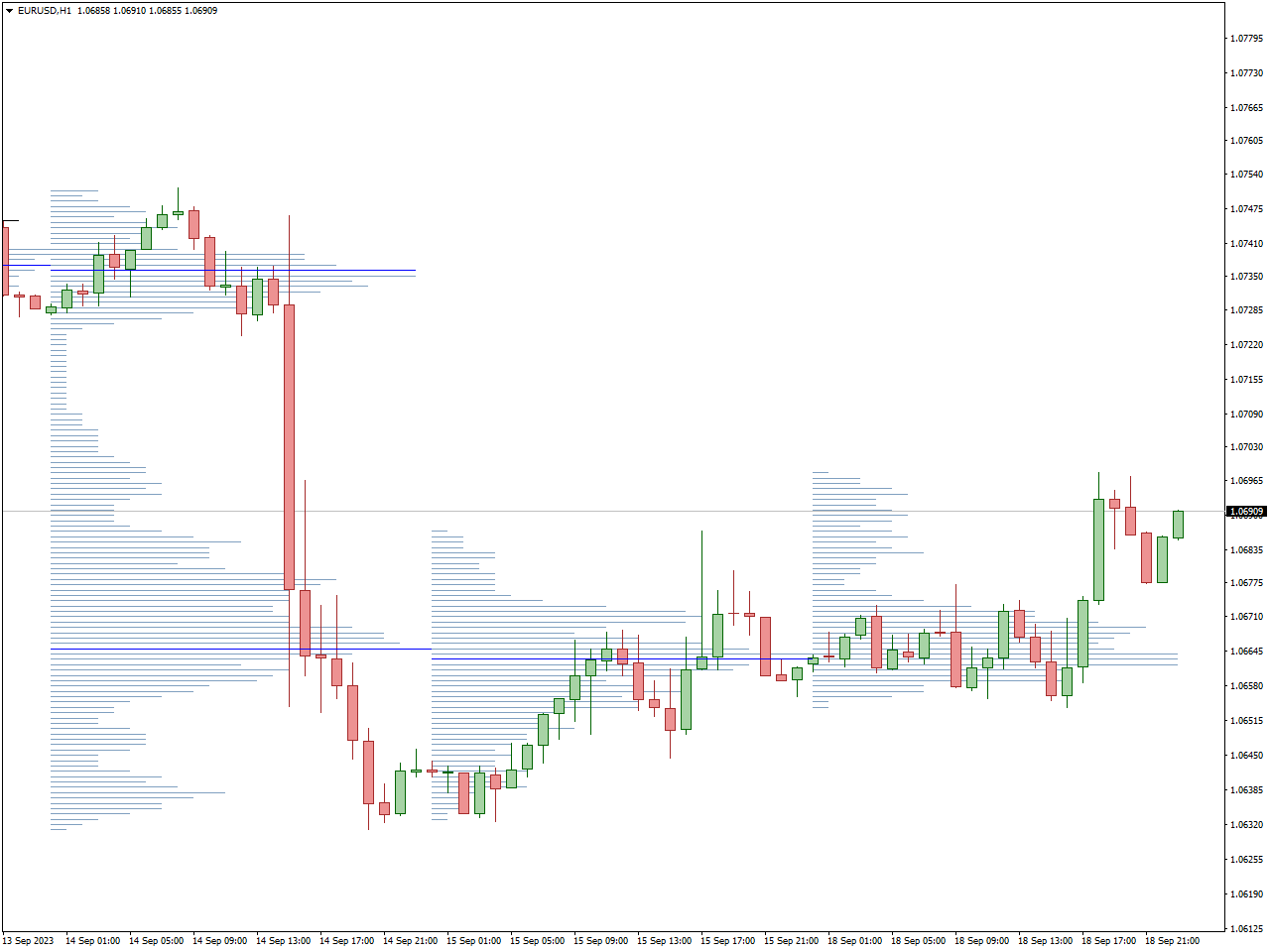
Swing Trading vs. Day Trading: Comparsion
Time Commitment: Swing trading is suitable for those who cannot dedicate their entire day to trading and prefer a more flexible schedule. In contrast, day trading is best for individuals who can commit to full-time trading and are comfortable making quick decisions.
Trading Frequency: Swing trading involves a lower frequency of trades, leading to potentially lower transaction costs. On the other hand, day trading features a higher frequency of trades with increased transaction costs, but it offers the potential for more consistent daily profits.
Skill and Experience: Swing trading may require less immediate market experience but demands a strong understanding of technical and fundamental analysis. Day trading, however, requires significant market experience, quick reflexes, and strong technical analysis skills.
Risk Management Strategies: Swing trading involves managing overnight risk and using stop-loss orders effectively. In contrast, day trading requires strict discipline in managing intraday volatility and implementing tight stop-losses.
Market Conditions: Swing trading is more suited to stable or trending markets where price swings can be captured over days or weeks. Day trading can be effective in both volatile and stable markets, focusing on capturing intraday price movements.
What should i choose?
Choosing between swing trading and day trading hinges on several factors that align with your trading goals, risk tolerance, and lifestyle preferences. Swing trading involves holding positions for days to weeks, aiming to capture larger price movements with fewer trades. It suits traders who prefer a more relaxed trading pace and cannot dedicate constant attention to the markets. This approach requires patience, discipline, and a strong understanding of technical and fundamental analysis to identify trends and potential reversals effectively. Conversely, day trading involves buying and selling within the same trading day, capitalizing on short-term price fluctuations. It appeals to those who thrive in fast-paced environments, possess advanced technical analysis skills, and can monitor markets closely throughout trading hours. Day trading offers the potential for frequent, modest gains but demands quick decision-making and risk management to navigate volatile market conditions. Ultimately, the choice between swing trading and day trading depends on your trading style, time commitment, risk appetite, and proficiency in market analysis.
Conclusion
Swing trading is an excellent choice for beginners due to its flexible schedule and lower frequency of trades, which reduces the pressure of constant market monitoring. This approach allows novice traders to develop their skills in technical and fundamental analysis gradually. Additionally, beginners can benefit from using forex signals, which provide insights and trade recommendations from experienced analysts, helping them make informed decisions. Understanding and analyzing market sentiment also plays a crucial role in swing trading, as it helps traders gauge the overall mood of the market and anticipate potential price movements. By combining these strategies, beginners can build a solid foundation in trading while managing risks effectively.
Day trading is a demanding but potentially rewarding approach, ideal for those who can commit to full-time trading and thrive in fast-paced environments. It requires a significant level of market experience, quick reflexes, and advanced technical analysis skills. The frequent trades and need for real-time decision-making can be challenging for beginners, but with disciplined risk management and strict adherence to stop-loss strategies, traders can mitigate risks effectively. Utilizing tools like intraday charts, volume analysis, and market orders, day traders aim to capitalize on short-term price movements and market volatility. For those willing to invest the time and effort, day trading offers the potential for consistent daily profits and a deep engagement with the financial markets.
Ultimately, the choice between swing trading and day trading depends on your personal preferences, time availability, risk tolerance, and trading experience. By understanding the key differences and considerations, you can choose the strategy that best aligns with your trading goals and lifestyle.

